Basement how to make ventilation yourself. Basement ventilation device of a private house: do-it-yourself cellar hood extraction.
The microclimate and comfortable living in a private house are largely influenced by the competently created ventilation of all its rooms and, in particular, the proper ventilation of the basement. Good ventilation in the basement of the house will eliminate excess moisture, protect against the appearance of fungi, mold and significantly extend the life of the house. When building a private house, many people pay too little attention to the ventilation of the basement, citing the complexity of the issue or the lack of necessary skills, trying to provide only the necessary minimum. In fact, creating a basement ventilation is quite simple, you just need a little desire, ability to use the tool and an understanding of how ventilation works.
Especially popular for low cost are metal-coated strips, which, however, limit the flexibility and yield of the foil. Foil systems The greatest advantage over bitumen tapes is their general mechanical properties, especially their high ductility, long service life and the ability to process under relatively adverse conditions. Since the resulting properties of the entire insulation substantially depend on the quality and leakage of joints and perforations, the relatively complex and technologically complex installation of this insulation is a drawback.
Basement ventilation device
In fact, ventilation is a system of pipes or shafts that provide the normal parameters of humidity, temperature and air exchange in the house. The ventilation of the basement of a private house can be forced and consist of a whole network of ventilation ducts with a supply device and an exhaust fan, and it can be natural and consist of a supply and exhaust pipe. To answer questions on how to make the ventilation of the basement, and which of the two types to choose, you need to know about the advantages and disadvantages of each, as well as design features.
The most widely used polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene materials. Spherical insulation An advantage is the ability to compact and form even very complex parts and permeability. On the contrary, the disadvantage is the relatively large complexity and complexity of providing the required thickness of the spatula. Great demands are also made on the surface on which the putty knife is applied. The resulting quality and integrity are so highly dependent on discipline and process procedures.
From the above requirements it is clear that the anti-district isolation itself often performs the function of isolating moisture in the soil. For these reasons, the additional cost of protecting radon is minimal. The Radon Insulation manual, which can be downloaded here or in the links at the end of this section. As already mentioned, with a very high radon index, it is necessary to add antitumor isolation to any other structure. Isolation limits only the diffusion of radon from the bowels to the internal air; at lower concentrations in the bowels, the obtained concentration of radon corresponds to the target value, but at extreme values \u200b\u200bof the radon index it already exceeds the limits.
Forced ventilation is suitable for homes with a large area, where in addition to the basement, ventilation also has to be provided for residential premises. Such ventilation consists of many elements, and not many can afford the costs of its purchase and installation.
The principle of operation of forced ventilation consists in the following. Air from the street is pumped into the system using a fan, where it is filtered, heated or cooled if necessary, and then, with the help of the same fans, it is fed further through the ventilation ducts into the premises.
The insulation used is a ventilation system under water or a ventilation air gap under the insulation. The task of drainage systems is to reduce the concentration of radon or below the base plate to create negative pressure in the bowels against the air pressure in the cabin. The drainage system consists of a system of perforated drainage pipes that are placed in the gravel layer under the foundation slab. To increase efficiency, it is advisable to release a drainage system through a vertical ventilation pipe with an exit over the roof.
Forced ventilation in the basement: photos

The forced ventilation system of the basement consists of the following elements:
- ventilation ducts;
- discharge unit of the furnace or air conditioner;
- air vent;
- air intake;
- air diffusers;
- tees summing flow.
The main disadvantages of forced ventilation are its high cost, the complexity of installation. Of the advantages it should be noted independence from external weather conditions, adjustable and high-quality air exchange.
Drainage systems can be passive or active. The objective of a ventilated air gap is to reduce the concentration of radon under insulation against radon or under pressure to internal pressure. These films create both an air gap and insulating insulation above it. Increased efficiency and reliability are achieved by ventilating the air gap through vertical pipelines above the roof of the building. In this case, it is recommended to use a fan to create and maintain a vacuum.
Finally, it should be noted that these preventive measures are more expensive, but because of the high concentration of radon in the bowels they are necessary. On the other hand, only a small percentage of buildings should be involved in such measures. In most cases, the building is located on a site in the low radon category, where classic waterproofing is used as an antitumor coating. The rest of the land belongs to the middle or lower category of the high-risk zone, where it is enough to protect the property only with an appropriately developed anti-cancer insulation, which then serves as a waterproofing.
In contrast to forced natural ventilation of the basement consists of only two main elements: supply and exhaust pipes. Natural ventilation has been known for a long time and is still popular because of its simplicity, and it does not require large financial expenses for its arrangement.
The principle of natural ventilationbased on the temperature difference inside and outside the basement, resulting in air movement. Thanks to this simple natural phenomenon, the air from the basement is drawn into the street, and fresh comes from the street. Unfortunately, the draft force of natural ventilation is strongly influenced by the wind, which can both strengthen and weaken the draft.
The basis for the project of antradradon measures for existing buildings is the result of a detailed radon diagnostics of the object, which determines the type, location and output of the radon source and its distribution through the object. Consistent and high-quality examination of the object in relation to the results of radon diagnostics can ultimately save a significant amount of money. The state subsidy for anti-radar measures for existing buildings cannot be considered as a means of improving the construction and technical condition of the facility, although in practice we often come across this approach.
Natural ventilation in the basement: photos

The basement ventilation system in a natural way consists of the following elements:
- supply channel;
- exhaust duct;
- vents.
The advantages of natural ventilation are the simplicity of its arrangement and low financial costs. Of the minuses, insufficient air exchange and a strong dependence on natural factors should be noted. The table below compares these two types of ventilation systems.
Investors who are not satisfied with the simple removal of radon and will require improvements in the state of construction should rely on such improvements to be made from their own resources. As already mentioned, measures in existing buildings are usually more expensive and more complicated than in new ones. However, if the concentration of radon in the air in the premises of an existing building is only slightly increased or if the living rooms are separated from the subsoil by a basement, there are a number of simple and cheap self-implementing measures. These measures are to seal the entry of radon into the building and increase internal air exchange.
Table number 1. Comparative characteristics of natural and forced ventilation

Today, pipes made of various materials are on the market. The most commonly used pipes are PVC and galvanized sheet. The use of PVC pipes has become very popular among those who are used to doing everything with their own hands. This popularity is due to the ease of installation.
Specific measures are very clearly described in the Handbook of Radon Measures in Existing Buildings, which can be downloaded here or in the links at the end of this section. If the concentration of radon in the air in an object’s room significantly exceeds this value, other, more expensive and more complex measures must be taken.
In many cases, a very effective and efficient measure can be an active emission of radon from the bowels under an object using several sampling points located so that air can move under the entire plan of the object’s earth. If it is not possible to make a hole in the floor from the inside, the space under the floor can also be let out from the outside through the foundation passage. Soil air is almost always exhausted by a fan. A condition of effectiveness is to ensure the integrity of the structure of the floor lying on the ground.
Unlike PVC, metal ventilation ducts will require some skill and skill, but their reliability will be much higher. Which of these materials to choose depends entirely on personal wishes and financial capabilities.
Due to low purchasing costs, high efficiency and quick implementation, this measure is relatively common and preferred. Another measure is the replacement of floor structures. Since this is a very expensive measure, it is only suitable for existing buildings where the contact rooms have living spaces and floors are in very poor condition and leak. In addition, the implementation takes a lot of time.
Indoor ventilation can also be used to reduce indoor concentration. Condition - relatively high quality and dense design. This is an effective but rather costly measure in terms of both acquisition and operation. Ventilation systems can be designed centrally for the entire facility or its parts.
How to make ventilation in the basement
As noted earlier, the choice of type of ventilation depends on the size of the basement. For large basements over 50 m2, it is recommended to equip forced ventilation. Basements with an area of \u200b\u200bup to 50 m2 will be perfectly ventilated with natural ventilation. An important point in the arrangement of ventilation is the planning of its placement in advance, even at the design stage of the house. This will greatly facilitate the installation as a whole. Of course, you can make ventilation in an already built house with a basement. In this case, you need to be prepared for a large amount of complex and labor-intensive work using special equipment for drilling holes and channels in the foundation, basement and ceilings to create ventilation ducts.
The advantage of this device is that the air conditioner does not disturb the user with noise, because it is located either on the roof or in the basement of the building. On the other hand, the disadvantage is the presence of very difficult to clean ducts, which must also be appropriately integrated into the interior. A significant advantage is the removal of a hygienically problematic duct and the ability to optimally adjust the power of the device in accordance with the needs of the room.
Building material radon can be an important source of radon in older buildings. The obligation of manufacturers to comply with limits and benchmarks in manufactured building materials began to be applied with the introduction of the Radon Program before this obligation was not. Therefore, some old building materials, especially from risky raw materials, can contribute to the overall concentration of radon in the air of a building.
Creating natural ventilation
Ideally, before arranging ventilation in the basement, you will have to prepare a ventilation scheme at the design stage of the house. It is necessary to take into account the volume of the room and the throughput of the ventilation ducts. For the supply and exhaust ventilation scheme, especially a lot will not be required. Just mark the installation location of the exhaust and supply pipes, as well as indicate their diameter. The pipes themselves should be located in opposite corners of the room.
The most effective way is to directly remove high-speed materials from the surface exhalation of radon. At the same time, however, this method is very expensive and not always applicable. Removal may be, as a rule, of the supporting structure. Although it is theoretically possible to replace load-bearing structures, this method is not cost-effective, since the costs are already comparable to the construction of a new building.
The disadvantage of this redevelopment is low efficiency and low service life due to the high tendency of such surface treatment to mechanical wear. A very effective and effective method of protection against radon from building materials is the active ventilation of the interior of the building. At the same time, it can also serve as a measure against radon from the bowels. If both sources of radon are in the building, this is preferred.
Basement ventilation scheme in a natural way: photo
The exhaust pipe hole is located under the ceiling, and the pipe itself is discharged 40 - 50 cm above the ridge of the roof of the house. The supply pipe is completely placed inside the basement so that its edge is 40 - 50 cm above the floor and the inlet is 40 - 50 cm above the ground. The diameter of the pipes affects the volume of air flow, and their height on the speed of movement. Unfortunately, natural ventilation is highly dependent on natural factors, so it’s almost impossible to get accurate calculations. The recommended pipe diameter of 12 cm for a room of 40 m2, while air exchange will be achieved about two volumes of the basement per hour. But it is better to use pipes of a larger diameter, this will somewhat reduce the dependence on natural factors and increase the rate of exchange of air in the room.
If groundwater is the source of radon in the house, the following precautions are taken: removing radon from the water using a special device or ensuring adequate ventilation of rooms with high water consumption so that radon does not enter the building. However, since old buildings are mainly connected to public water supply, the problem of using radon from tap water is not fulfilled due to the obligation of suppliers to comply with the limits and indicative values \u200b\u200bin the supplied water.
Neopin foil is a high density polyethylene film with semi-conical protrusions that allow air to flow. Neopin foil has a wide range of applications both in new structures, where it serves mainly as drainage and mechanical protection of the foundation structure, and in reconstructions, where it is especially designed for ventilation and drainage of existing building structures. Neopin foil effectively prevents the penetration of radon and allows its ventilation, nopic foil is ideal for draining the house, draining the basement, redefining wet walls and floors.
To create natural ventilation of the basement with your own hands, you will need a minimum amount of materials. Basically it will be metal or plastic pipes and baffles, as well as pipe clamps. If the ventilation of the basement is done during the construction phase of the house, then there will not be any special problems. It will only be necessary to create holes of the required diameter in the construction of the house. Then install pipes in them and fix them inside with mounting foam or cement-sand mortar. But in case you have to do ventilation in an already built house, you will first have to break through the channels for installing pipes. The easiest option is to partially dig out the foundation, punch channels in it, then install pipes in them and fix them there. In this case, the exhaust pipe is discharged above the roof level, is fixed to the wall with clamps fixed with dowels in the holes, and is closed by a deflector on top, which protects it from precipitation inside. The supply pipe is only partially displayed on the street; it is protected from above by a metal mesh and a deflector. Inside, the supply pipe is fixed with clamps to the wall.
Neopin foil can also be used as a replacement for an insulating trough to protect the base layer of waterproofing. Another use method is two-stage radon penetration protection. The first step is to create a ventilated air gap, a second-stage barrier impermeable to polyethylene. Radon is an odorless, colorless gas, and its presence in the building cannot be easily recognized. Based on the determination of concentrations, it is usually necessary to move on to the selection of a suitable reduction method that prevents or reduces the concentration of radon.
Important! Condensate can accumulate in the supply pipe, so a special moisture collector with a tap is installed at its end to drain the excess.
Creating forced ventilation
As in the case of natural ventilation, the forced draft must be prepared in advance. The project itself should contain calculations on the hourly rate of air exchange in the room and its volume. The air exchange rate is calculated on the basis of a flow rate of 2 m3 per 1 m2 of area per hour. Multiplying the volume of the room by the rate of air exchange, we obtain the necessary fan performance. Another parameter for selecting a fan is the pressure loss in the duct, so it is better to choose a fan with a margin in order to minimize losses in the system. For clarity, we will analyze an example for a room with a volume of 100 m3. The length of the ventilation channel is 10 m, diameter 100 mm.
The appropriate developer should always indicate the appropriate method. Neopin foil with its design allows you to create a two-stage protection against the penetration of radon gases. Two-stage protection means creating a ventilated air gap between the base and the floor structure, then the second step is to create a waterproof barrier made of plastic film. Thus, the barrier prevents the penetration of moisture into the building.
This system can be used for moderate to high risk of exposure to radon in soil air. If proper waterproofing of the basement is not performed, moisture penetrates the wall into the interior of the building. This problem can be solved using. The principle of the method is to separate the wet basement from the moist soil. Tapes in the film create an air gap between the masonry and the soil. Moisture in the soil does not have access to the wall. Moisture already contained in the wall, or moisture entering the basement wall from the inside, is discharged and transported to the pipeline drain.
Table number 2. Calculation of pressure loss per 1 m of the air channel

The fan power will be equal to 100 * 2 \u003d 200 m3 / hour. In the above diagram, we find the horizontal intersection point of 200 m3 / hour and the diagonal (channel diameter 100 mm.). Lowering the straight line down vertically, we get a pressure loss of 1 m, and it will be 8 Pa. For the entire air channel, the loss will be 8 Pa * 10 m \u003d 80 Pa. Now it remains only to find a fan that, with a pressure loss of 80 Pa, will have a capacity of 200 m3 / hour.
As noted earlier, it is advisable to equip forced ventilation in houses with a large area that require a single centralized ventilation system, and basement ventilation will be only part of it. Calculations and the creation of such a project require specialized knowledge, so it would be better to turn to specialists for help. Of course, you can organize forced ventilation only in the basement, and you can deal with this yourself.
Basement forced ventilation scheme: photo

Important! To ensure ventilation of the basement alone, it is possible to exclude from the system such an element as the discharge unit of the furnace or air conditioner. To remove or leave this element depends on the requirements for ventilation of the basement and the intended use of the basement itself.
The installation of forced ventilation air channels is not much different from the natural installation, and how this is done can be read above. The main difference is in the following points. Firstly, the exhaust and supply pipes can be placed at a level of 50 cm above the ground. Secondly, the fans themselves are installed on the pipes themselves, one on the supply and one on the exhaust. This may require the installation of discharge units.
Video: forced ventilation
Creating the ventilation of the basement with your own hands, it is necessary to take into account many factors, from the target operating conditions of the room to the natural conditions in the region where the house is built. The arrangement of ventilation itself is not particularly difficult for those who are used to doing everything with their own hands. The main thing is to carry out all the work carefully and without haste.
That is why basement ventilation in a private house ─ is considered one of the main systems in any private house. The basement of such a house should not be hazardous to health, although the landlord does not live in it permanently. The importance of basement ventilation is difficult to overestimate, since not only the health of the body, but also the microclimate, the temperature regime of the entire structure, as well as the duration of the operation of the house, directly depend on it.
Ventilation scheme
Based on the purpose of the basement, an appropriate ventilation scheme is selected.
The problem of stagnation of air masses can be solved quite simply due to the effect of air movement due to temperature differences outside the house and in the basement. The natural diagram is shown in the figure below.
In addition to this scheme, there is a more complex and ramified scheme of mechanical ventilation for large areas of the basement, and at the same time rooms of the house. It is called forced-air or mechanical. It has more components than natural, and there is always an electric fan (air conditioning) or several such devices.
Types of ventilation
Ventilation in is a device of air ducts (pipes) and channels for (mines) according to a certain scheme. As mentioned above, there are two types of ventilation: natural (supply / exhaust) and forced (mechanical).
Their principle of functioning is different. If the first is based on the action of the natural laws of physics and does not require human intervention during operation, the second is possible only if there is an electric fan or several such units.
Basement ventilation device in a private house
Basement ventilation in a private house is organized in the following ways:
- Through small windows in the base ─ air ducts (least expensive ventilation). The effectiveness of this scheme always depends on the direction and strength of the wind, the temperature of the street air.

Calculation of product area: 1/400 of the total basement area. Plus, the following are taken into account:
- foundation depth;
- proximity of groundwater and soil type;
- the main direction of the winds;
- precipitation intensity at different times of the year;
- temperature differences;
- holes should be at least 125 mm in diameter.
Natural ventilation can be controlled. To do this, valves are installed on the vents.
- Through the supply and exhaust (also natural). The microclimate in any basement of a wooden house is perfectly supported by a supply and exhaust system. It consists of 2 ducts. One by one the air mass enters from the outside, by the second it moves out.
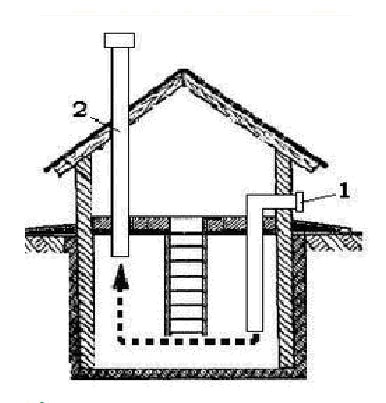
Supply / exhaust ventilation
1-supply pipe; 2 - exhaust pipe
The lower part of the supply pipe is fixed half a meter from the basement floor, the upper ─ protrudes above the soil surface per meter. The beginning of the exhaust pipe is raised one and a half meters above the floor, the upper end protrudes half a meter above the ridge of the roof. Both pipes are placed on opposite sides of the basement. It is recommended to arrange valves on them to control the intensity of ventilation. Pipes for ventilation usually have a diameter of 10-15 mm.
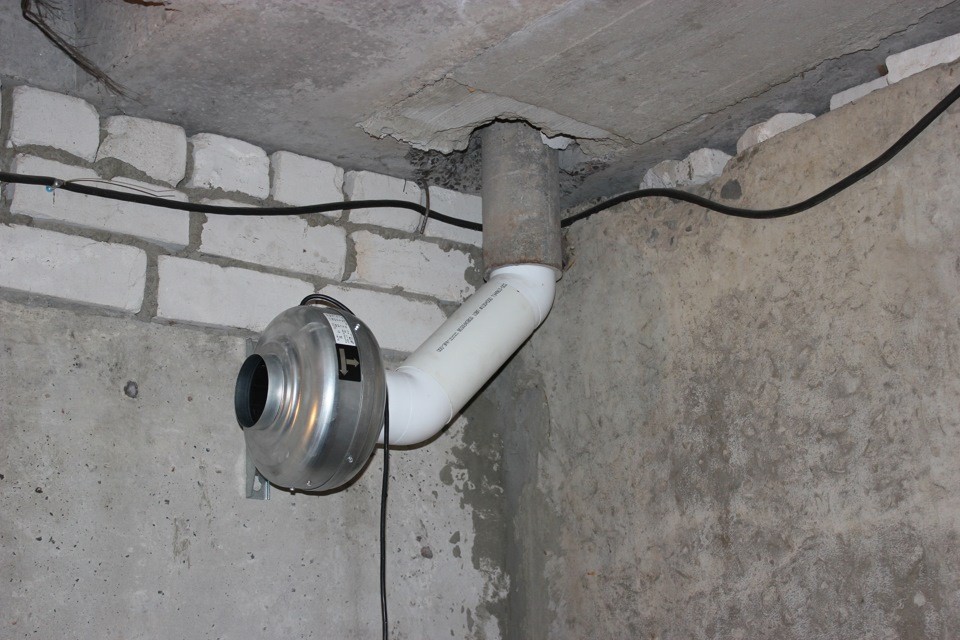
- With the help of forced ventilation (the most expensive ventilation). How is artificial air exchange created? When the basement’s natural ventilation system cannot be installed, or its capacity is not enough, air stagnation is fought with the help of a forced ventilation system or forced-air / forced (mechanical) ventilation. In it, the air extract is carried out by an electric fan connected to the exhaust pipe.
Forced ventilation scheme:
- ventilation ducts
- discharge unit of a home stove or air conditioner,
- air intake
- air outlet
- air diffusers,
- thread mixing tees.
Such a ventilation system can also be called composite, since the forced system is turned on as necessary, and the rest of the time it works in conjunction with the natural one.

If the basement is large, installs two electric fans ─ exhaust and supply. Their capacities are consistent, and pipe diameters are calculated. Any pipes are taken: plastic, metal, asbestos-cement. You can use ready-made ducts. This system works for both small cellars and large basements.
The operating mode of the described system is designed for the whole year, since it is not affected by the temperature difference. This feature is its main difference from the natural way of ventilation of the basement.
Conclusion
It doesn’t draw damp from the floor, the air is comfortable in the house, and the potatoes are stored without germinating all winter, which means that the ventilation of the basement in a private house functions correctly. It provides directional movement of air masses. Due to the constant exchange of air between the external air and the basement, a stable humidity and temperature are established in the building. Prerequisites arise for the proper storage of supplies and vegetables; mold and fungus do not appear.
If air exchange is absent or insufficient, use the basement as a pantry is useless. Moreover, the dangers of dampness are exposed to the foundation and overlap. But the main danger awaiting the inhabitants of the house with a warm basement, but without ─ is a high probability of a fire or even explosion due to the high concentration of carbon dioxide. This gas is emitted during the operation of heating devices, often installed in the basement or basement. That is why basement ventilation in a private house is simply necessary.

